
The Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) is an international treaty that facilitates the process of filing patent applications in multiple countries. By filing one international patent application under the PCT, applicants can seek protection for an invention in a large number of countries.
What is Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT)
The Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) is an international treaty established in 1970, managed by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO). It facilitates the process of international patent filing in multiple countries. The PCT simplifies the process of seeking patent protection in multiple countries by filing a single international patent application.
Contracting Country in Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT)
There are more than 155 Contracting Countries in Patent Cooperation Treaty. To learn more about contracting countries along with their name and code, visit PCT contracting countries.
Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) Application Process
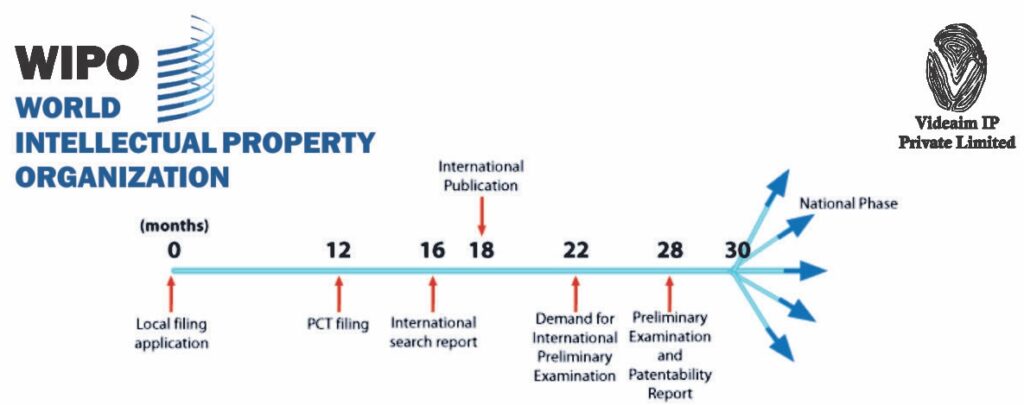
Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) application process:
International Application: An applicant files an international patent application with a national or regional patent office or an international patent office (referred to as the “receiving office”).
International Search: The international patent application is subjected to an international search conducted by an International Searching Authority (ISA) chosen by the applicant from a list of participating patent offices. The ISA searches prior art documents to assess the novelty and inventiveness of the invention claimed in the application.
International Publication: The international application is ready to publish in 18 months after the priority date (the filing date of the first application in any country). This publication makes the details of the invention publicly available.
Optional International Preliminary Examination (Optional): After the international search, the applicant can request an international preliminary examination to obtain a more detailed examination of the patentability of the invention.
National Phase: After the international phase, the applicant needs to enter the national phase by filing separate applications in each desired country or region within 30 or 31 months from the priority date, depending on the country.
Conclusion
It’s important to note that the PCT does not grant patents itself; it merely streamlines the process of seeking patent protection in multiple countries.
Applicant need to be make their PCT application available to a national phase entry in respective regional patent offices to obtain patent rights.
After making national phase entry in specific countries, the applicant needs to apply for examination in each individual country’s patent office and granting of patents remains under the control of the regional patent offices.
