
Understanding Freedom to Operate (FTO)
Even at an early stage of planning and developing a technology or invention, a company’s main objective is to patent the technology and commercialize it to make profit. Seldom do inventors or entrepreneurs pay attention whether the recently developed technology is likely to infringe any existing enforceable patent. Technology domain wherein exclusive patenting is the norm one has to really be careful if the commercialization of the technology is infringing someone else’s technology or is blocked by someone else’s technology.
FTO or Freedom to operate is a risk management tool that contemplates likelihood of infringement or litigation, and whether there is freedom to operate a patent or claim or invention. In simpler words it determines if you would infringe any third party’s granted patent in India, For example: if you have a formulation that is an improvement, so you usually add to a base formulation and show an improvement to get a patent.
A+B+C+D+E = 20% absorption than the base technology, A+B+C comprises the base technology, wherein D+E is improvement. In this case if any unauthorized use is made of A+B+C even though an improvement in the form of D+E is made, it is an infringement.
What is the difference between prior art search, Patentability and FTO search?
The basic difference is the focus of search, let’s discuss an example to understand the concept better.
Illustration: A 3 point seat belt system was invented in 1960. The advantage of the system is protection offered by it is almost 60% more effective than a 2 point seat belt as the upper body is also restrained.
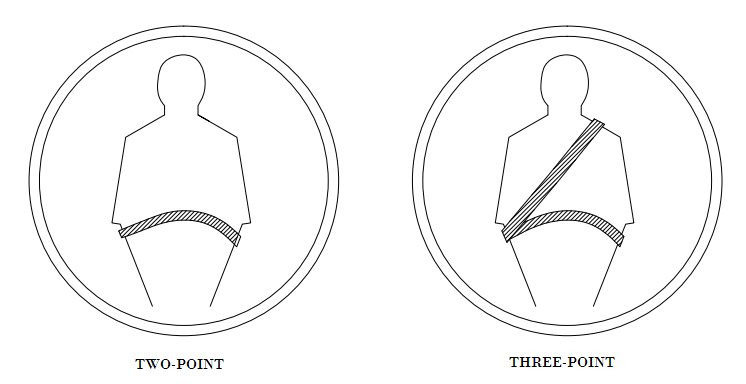
Prior Art Search: Now the focus of a prior art search shall pertain in establishing the novelty, hence the researcher would try and find out if there is a 3 point system present in the public domain, it would provide all the citations that has 3 point belt system. If no exact 3 point car seat belt is available then the invention would be deemed to be novel or in other words novelty is established.
Prior art search results:
Patentability search: Patentability search is focused in establishing Novelty by analysing relevant citations and also determining obviousness of an invention for a person skilled in the art, which would include enlisting the citations with seat belts having 2 or more point. This is to check if by combining 2 or more citation, someone can draw an obvious skill of creating 3 point seat belts without any undue diligence. More specifically, can different citations elucidating 2 point seat belts can be combined to teach a person skilled in the art to make 3 point seat belts with same technical advantage that is an obvious combination of the prior art.
Freedom to operate: The search strategy adopted for FTO is more focussed on establishing the operative freedom which shall include claim analysis of all the 2 point seat belts and categorization of patents to indicate the threat level by infringement.The differentiating feature from the other searches is that it is jurisdiction specific (i.e. done for a specific country) and includes the patents that are still enforceable in a particular jurisdiction or country, i.e. have not completed 20 years, annuities have been paid and are not invalidated and a detailed claim analysis determining the scope of the claims.
What are the options if the freedom is not absolute or limited?
Licensing In: Licensing In means taking license or obtaining authorization from a third party for a patent or technology, for specific acts over a negotiated period of time and for specific remuneration negotiated for lump sum upfront payment or periodic royalties.
Patent Purchasing: Patent Purchasing means purchasing the ownership rights of a patent and assigning all the rights of an owner.
Cross-licensing: A cross–licensing is as the name suggests is licensing between two patent owners providing each other licenses so that both the parties have a patent portfolio and both of them have the freedom to utilize each other’s patents. It involves two or more companies exchanging licenses so as to be able to use certain patents owned by the other parties. Patent exchange helps the parties to create a patent portfolio, increase valuation and also implement improved product line.
Inventing around: Inventing around as the name suggests means “invent around” the cited invention .e. coming up the formulation that obviates the components or features used in the prior art. Inventing around is not an easy task especially at the later stage as financial resources and time are consumed. Hence, it is advisable to undertake FTO at an early stage of development.
IP acts as an impetus for growth and is paramount consideration for an outside investor when it comes to providing capital. This is a known fact acknowledged by all the technology driven companies or start-ups.Hence, anytechnology driven start-upor company looking for future investmentare conscious enough to generate and protect technology aspatents. A granted patent provides a clear message to an investorabout the uniqueness of the product or process, and its possibility to create a space for its in market with less competition. In case a patent is pending a prior art search or patentability search provides a fair idea about the uniqueness. However, what most companies and start-ups do not realise that investors are also looking for operative freedom of the technology. An investor may deter from investing in a company that do not have operative freedom as the company is liable to be sued for patent infringement.
Even when a company is launching a new product such operative freedom is necessary so that one does not infringe someone else’s patent and is dragged into litigation. Therefore, at an early stage of development if one is looking to improve the technology or utilize a state of the art technology as the base technology then operative freedom needs to be determined and negotiated.
