
Patenting trends in Bitcoin and blockchain technologies reflect the growing interest and investment in decentralized technologies. Bitcoin and blockchain technologies have seen a significant rise in patent filings globally, with major contributions from countries like China and the United States.
Leading Countries with Blockchain Patents
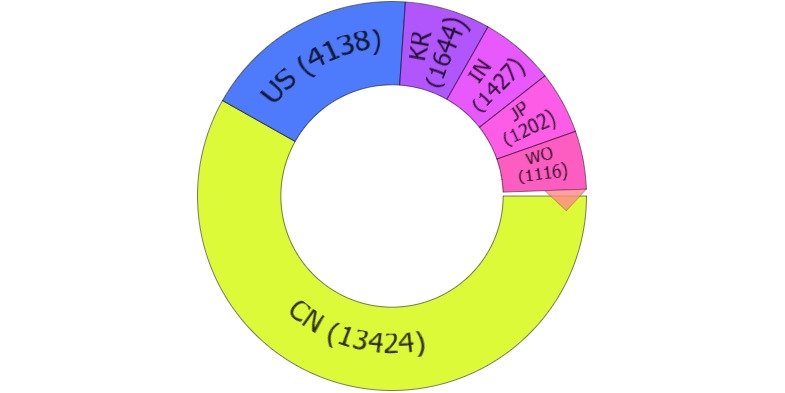
In 2020, China led the way, with 17 of the top 20 companies filing blockchain patent applications based there. Alibaba Group topped the list with 2,542 patents filed during that period.
In the United States, the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) has been actively granting patents related to blockchain technologies. The number of issued patents increased from 3 in 2016 to a peak of 1,854 in 2022. However, there was a projected decline to 1,535 patents in 2023, indicating a 17% drop.
India in Bitcoin and Blockchain Technologies
In India, the patenting landscape for blockchain technologies is evolving. The Indian Patent Office has granted patents for blockchain-based inventions, particularly when they provide technical solutions to technical problems, thereby offering a practical application or an improved technical effect.
A notable example is the Indian startup Grow Digi, which was granted two patents for a sector-agnostic blockchain technology layer. Their innovation reportedly reduces data storage requirements by about 95% and decreases transaction times from a minimum of 5 seconds to less than 300 milliseconds.
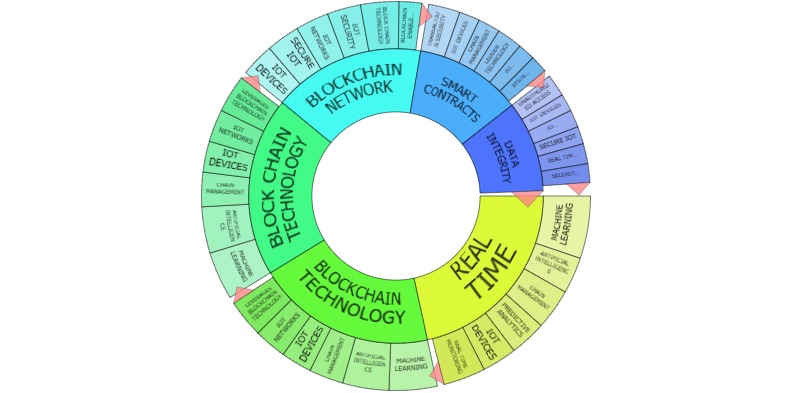
Relationship Between Bitcoin and Blockchain Technologies
- Blockchain as Bitcoin’s Foundation: The Bitcoin blockchain is the ledger where all Bitcoin transactions are recorded. Without blockchain, Bitcoin would not function as a decentralized currency.
- Blockchain Beyond Bitcoin: While blockchain was initially developed for Bitcoin, the technology has since been adapted for various other purposes, such as smart contracts, supply chain management, healthcare, and more.
- Decentralization: Both Bitcoin and blockchain emphasize decentralization, removing the need for intermediaries like banks or central authorities.
Conclusion
It’s important to note that the patentability of blockchain-related inventions in India is subject to certain legal interpretations. Section 3(k) of the Indian Patents Act excludes mathematical methods, business methods, algorithms, and computer programs per se from patentability. However, if a blockchain-based invention demonstrates a technical advancement or provides a technical solution, it may be considered patentable.
Overall, while the global landscape for blockchain and bitcoin-related patents is robust and growing, India’s patent regime is gradually adapting to accommodate such technological advancements, with a focus on technical contributions and practical applications.
